What Is a Water Borehole?
A water borehole is a drilling rig dug deep into the earth that connects with natural aquifers beneath the soil. Some water boreholes for test water quality, geological studies on soil samples, or irrigation purposes. Most of the time, it is simply access to pure water. Borehole water is in many ways like well water, and it is usually clean and healthy to drink. The drilling process includes drilling pipes and casings to protect against contamination.
Getting drinking water is the main purpose of a water borehole.
Bore drilling is a common way of getting into the earth’s innermost resources. Boreholes are common for a variety of purposes, including soil sampling, geological surveying, and natural gas extraction. Water boreholes are different from dug wells in many respects. The use of a drilling rig. There are several different types of drilling rigs available depending on the project, but most are portable and operate with a motorized engine, winch pull, and cable extraction system.
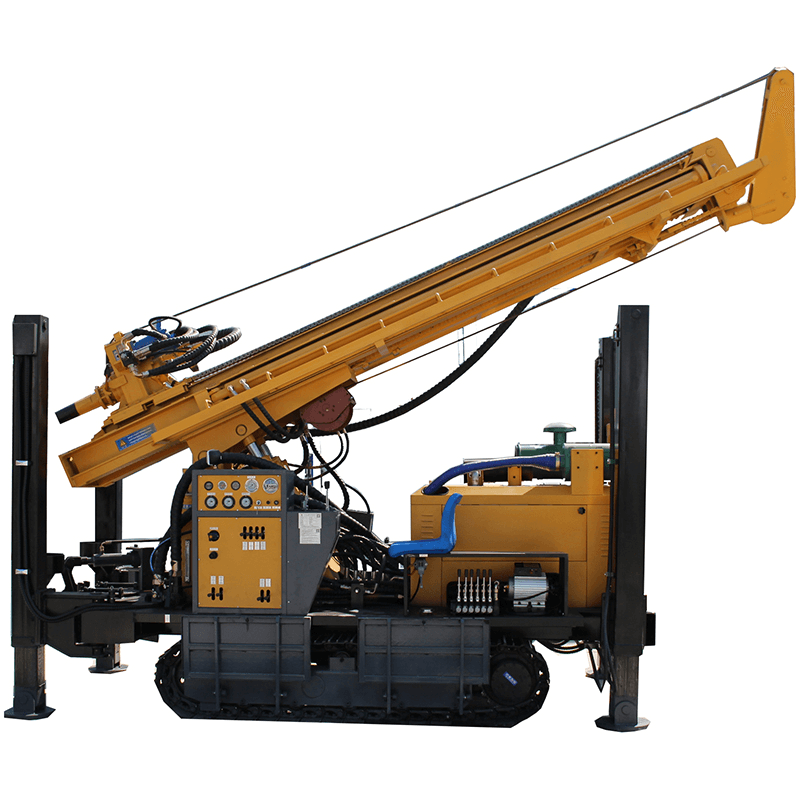
Check the types of drilling rigs in the products list, click here.
The drilling rig can usually be programmed to drill a precise dimension of the borehole as well. As a driller knows where water is under the ground, only program the rig and wait. This process often takes a little time to be successful. In most places, any hole dug deep enough will reach the water at some point. Where the water is located can vary tremendously from place to place. Drillers often use geological surveys and water detectors to find the precise location at any given site.
The main usage of a water borehole is to access pure water.
Sealing the borehole as soon as drilling is complete and proper sealing is very important to prevent water contamination. A water borehole is used by small communities or by a family. Water access through boreholes for a family is most common in rural areas where there are no pure water systems. Boreholes are sometimes provided pure water to the entire rural area or the whole village. Not all boreholes are used to provide drinking water, sometimes for geological study or irrigation.

